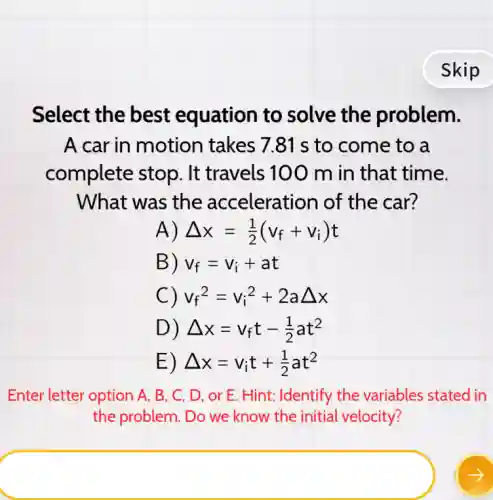
Select the best equation to solve the problem. A car in motion takes 7.81 s to come to a complete stop . It travels 100 m in that time. What was the acceleration of the car? A) Delta x=(1)/(2)(v_(f)+v_(i))t B) v_(f)=v_(i)+at C) v_(f)^2=v_(i)^2+2aDelta x D) Delta x=v_(f)t-(1)/(2)at^2 E) Delta x=v_(i)t+(1)/(2)at^2 Enter letter option A . B. C, D, or E. Hint: Identify the variables stated in the problem. Do we know the initial velocity?
Solution4.4(203 votes)
Answer
Explanation
Similar Questions
The branch of biomechanics that deals with the aspects of moving systems is known as dynamics. kinetics. mobility. kinematics.
A radioactive substance decays exponentially. A scientist begins with 140 milligrams of a radioactive substance. After 24 hours 70 mg of the substance remains. How many milligrams will remain after 27 hours? $\square $ mg Give your answer accurate to at least one decimal place Question Help: Video
When a forklift is loaded, where is its center of gravity? A. Under the operator B. At the center of the forklift C. Varies based on the combined centers of gravity of the forklift and the load D. At the center of the forks
Which of these statements is most likely correct about a weak nuclear force? (2 points) It binds electrons and protons. It is a repulsive force. It is an attractive force. It binds protons and neutrons.
Living and Nonliving substances obey all of the answers the 1st law of thermodynamics. the 2nd law of thermodynamics. the law of gravity.
Which side of the electromagnetic spectrum has shorter waveiengths? $\square $ Which side of the electromagnetic spectrum has higher energy? $\square $ Which side of the electromagnetic spectrum has higher frequencies? $\square $ blue
Physics is explicitly involved in studying which of these activities? A. the mixing of metals to form an alloy B. the metabolic functions of a living organism C. the motion of a spacecraft under gravitational influence D. the depletion of the atmospheric ozone layer due to pollutants E. the killing of cancerous cells by radiation therapy
Outdoors, shadows are longest at what time of day? Midnight Sunrise and sunset Noon 10 a.m.
Whose laws of motion became the basic building blocks for our understanding of the functioning of the universe? Johannes Gutenberg Martin Luther Isaac Newton Francis Bacon Rewatch
What happens if supercells form too close to each other? They will cause a derecho That's the plot of Sharknado They merge into a huge supercell Their outflows may interact and they may dissipate









