9. (6 points)Using two or more of the following reactions. N2(g)+3/2O2(g)arrow N2O3(g)Delta H=+83.7kJ N2(g)+O2(g)arrow 2NO(g)Delta H=+180.4kJ 1/2N2(g)+O2(g)arrow NO2(g)Delta H=+33.2kJ Determine the Delta H^circ of the following reaction: NO(g)+NO2(g)arrow N2O3(g)Delta H=?
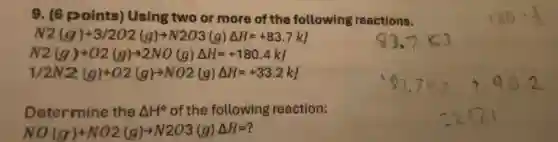
Solution4.7(202 votes)
Answer
Explanation
Similar Questions
2. Can you determine conclusively that an unknown substance contains only magnetite by using only a magnet? Explain your answer. __
Before you go, which type of molecule would you choose to be the anode in a lithium battery? a) The metal with the most negative potential b) It does not matter since lithium's potential is so negative c) The metal with the most positive potential d) Another lithium compound
Multiple Choice Question If phenol red is added to a solution with a pH of 9.0, it will appear __ pink-red yellow
Approved laboratory safety glasses must be worn - when lighting a bunsen burner at all times while dispensing liquids while centrifuging liquids Clear my selection
What precipitate forms when mixing silver(I)nitrate and sodium chloride? silver(I) chloride sodium nitrate no precipitate forms
2. Using your knowledge of chemistry and the information in Reference Table H.which statement concerning propanone and water at $50^{\circ }C$ is true? (A) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (B) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water. (C) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (D) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water.
An exothermic reaction is one in which $\square $ Reactions $\square $ lose energy without losing heat.
Fill in the Blank Question The reaction between an acid and a base is called a(n) $\square $ reaction when the product is a neutral solution of water and a soluble ionic compound called a(n) $\square $ Need help? Review these concept resources. Read About the Concept
Calculate the molar mass $\square $ of $C_{10}H_{16}ClN$ (meth). Indicate if the molar mass is equivalent $\square $ to a FW or a MW.
Part I: Unit Conversions.Show all work (known and unknown, and dimensional analysis - including units! Write your answers in the boxes provided. Unit Test: Dimensional Analysis and Mole Convers 1. Find the number of minutes in 25 years, assuming that $1year=365days$ K:25 years 2. The driving distance from Spokane to Seattle is 479,000 meters. Convert this distance to miles given $1m=100cm,1in=2.54cm,12in=1ft,$ and $1mi=5280ft$ $\square $ Part II: Mole Conversions . Show all work (known and unknown, and dimensional analysis - including units! Write your answers in the boxes provided. 3. A sample contains $9.2\times 10^{22}$ atoms of beryllium (Be)How many moles is this? $\square $ 4. The formula for Aluminum Carbonate is $Al_{2}(CO_{3})_{3}$ What is the molar mass of aluminum carbonate? $\square $









