((1)/(27))^x^(2)=(9^3x+8)((1)/(81))^x^(2)
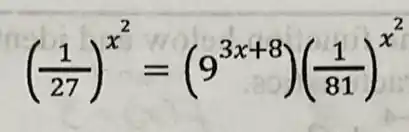
Solution4.1(230 votes)
Answer
Explanation
Similar Questions
Line can be used as a tool to: Select an Answer A. demarcate boundaries B. imply direction C. define shapes D. all of the other answers
On average how many times will a volleyball player jump in one game. $300;200;400;500$ 300 400 500 200
16. (Trig or special right triangles) OPEN RESPONSE A 10-foot-long ladder leans against a wall so that the ladder and the wall form a $30^{\circ }$ angle. What is the distance to the nearest tenth of a foot from the ground to the point where the ladder touches the wall?
Solve the following polynomials using synthetic division and then solving the quadratic expression. Show your work. 7) $y=x^{4}+x^{3}-3x^{2}+3x-18$ 8) $y=x^{4}-5x^{3}-2x^{2}+19x+15$
If 500 tickets are sold and there are 10 winning tickets, what is the probability of losing?
Find the following in radians without using a calculator. $cos^{-1}(-\frac {\sqrt {2}}{2})=\frac {[?]\pi }{[\quad ]}$
Given one factor, find the solutions to the polynomial. Use synthetic or long division. Show work. 3) $y=4x^{3}-12x^{2}-x+15$ factor: $2x-3$ $y=x^{4}-8x^{3}-23x^{2}+30x$ factor: $x-1$
Which number is NOT in the solution set of $-3\gt x\gt -7$ A. $-4$ B. $-2$ C. $-5$ D. $-6$
Evaluate the integral. $\int _{6}^{8}\frac {x}{x^{2}+4x+20}dx$ $\square $
Solve the equation by factoring: $x^{2}-5x-6=0$ $x=\{ 2,-3\} $ $x=\{ -2,3\} $ $x=\{ -1,6\} $ $x=\{ 6,1\} $









